Why Does Polyurethane Beat Cement Grout for Void Filling?
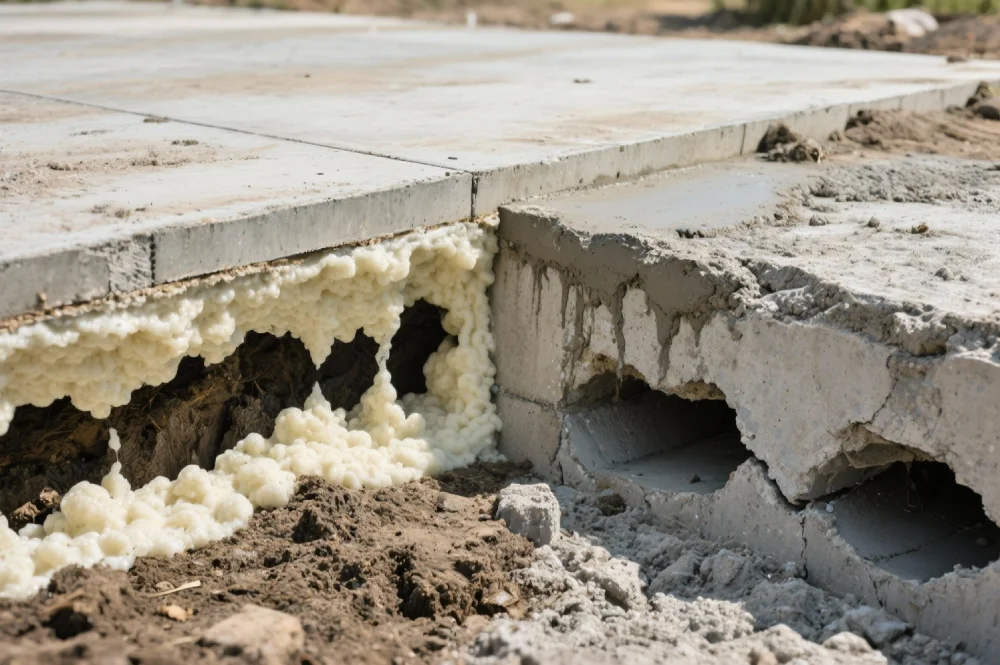

Polyurethane beats cement grout for void filling because it offers superior expansion characteristics, lighter weight, faster cure times, and better water resistance properties. While cement grout is heavy, slow to cure, and prone to shrinkage, polyurethane foam expands during injection to fill voids completely and provides immediate structural support with minimal added weight.
The expanding foam creates uniform fills that prevent future settlement issues while requiring smaller injection holes and causing less disruption to operations. These characteristics make polyurethane more efficient and cost-effective for most void filling applications.
Professional polyurethane grouting services in Texas and nationwide utilize these material advantages to provide superior void filling results with reduced project time, lower disruption, and better long-term performance compared to traditional cement-based approaches.
Key Takeaways
- Polyurethane foam expands during injection to fill voids completely and uniformly, while cement grout cannot expand and may shrink over time creating gaps.
- Weight differences are dramatic: polyurethane weighs 2-20 lb/ft³ compared to cement grout at ~120 lb/ft³, reducing load on underlying soils and structures.
- Cure time advantages allow polyurethane to provide structural support within minutes compared to hours required for cement grout to achieve adequate strength.
- Water resistance properties of closed-cell polyurethane prevent erosion and infiltration, while cement grout offers only moderate water resistance and can deteriorate.
- Installation disruption is minimized with polyurethane's small injection holes compared to larger access requirements for cement grout applications.
- Long-term durability and adhesion properties of polyurethane provide superior performance with fewer maintenance requirements than cement-based materials.
Material Property Comparison
Understanding the fundamental differences between polyurethane and cement grout helps explain why polyurethane consistently outperforms cement for void filling applications.
Weight and Density Differences
The dramatic weight difference between these materials significantly impacts their suitability for void filling applications, particularly in areas with weak or sensitive soils.
| Material Property | Polyurethane Foam | Cement Grout | Impact on Performance |
| Density | 2-20 lb/ft³ | ~120 lb/ft³ | 6-60x lighter load |
| Structural Impact | Minimal added weight | Significant load increase | Prevents further settlement |
| Soil Stress | Negligible increase | Major stress addition | Reduces compaction risk |
| Foundation Loading | No overloading risk | May exceed design limits | Maintains structural integrity |
Expansion and Fill Characteristics
Polyurethane's ability to expand during injection creates superior void filling compared to cement grout's static placement characteristics.
According to construction materials research, polyurethane foams can expand to fill complex void geometries that would be impossible to reach with non-expanding materials like cement grout.
Expansion Benefits:
- Reaches irregular void shapes and narrow cracks completely
- Ensures uniform contact with all void surfaces
- Eliminates air pockets and incomplete filling
- Provides immediate structural support through expansion pressure
- Adapts to complex subsurface geometries automatically
Cure Time and Service Restoration
Rapid cure times allow polyurethane applications to restore service quickly, minimizing disruption to operations and reducing project costs.
Cure Time Comparison:
- Polyurethane: Initial cure in 15-30 minutes, full strength within 2-4 hours
- Cement grout: Initial set in 30-60 minutes, full strength in 24-28 days
- Service restoration: Polyurethane allows immediate use, cement requires extended waiting
- Project scheduling: Polyurethane enables same-day completion, cement requires multi-day scheduling
Performance Advantages in Void Filling
Polyurethane's superior performance characteristics translate into measurable advantages for void filling applications across various infrastructure scenarios.
Water Resistance and Environmental Durability
The closed-cell structure of polyurethane foam provides excellent water resistance that prevents erosion and maintains structural integrity in wet conditions.
Texas infrastructure faces particular challenges from seasonal flooding, high groundwater, and expansive clay soils that make water resistance critical for long-term performance.
Water Resistance Comparison:
- Polyurethane: Hydrophobic, closed-cell structure prevents water absorption
- Cement grout: Porous, absorbs water leading to freeze-thaw damage
- Erosion resistance: Polyurethane maintains integrity, cement may wash out
- Chemical resistance: Polyurethane resists most chemicals, cement vulnerable to acid attack
Adhesion and Bonding Strength
Strong adhesion to existing materials ensures polyurethane void fills remain effective under dynamic loading and environmental stresses.
According to geotechnical engineering studies, polyurethane's chemical bonding mechanism provides superior long-term adhesion compared to cement grout's mechanical bonding alone.
| Bonding Aspect | Polyurethane | Cement Grout | Long-Term Impact |
| Adhesion Mechanism | Chemical bonding | Mechanical bonding | Superior durability |
| Bond Strength | High tensile strength | Compression only | Better crack resistance |
| Flexibility | Accommodates movement | Rigid, cracks under stress | Maintains seal integrity |
| Interface Failure | Rare occurrence | Common failure mode | Fewer repairs needed |
Settlement Prevention and Structural Support
Polyurethane's lightweight nature combined with excellent structural properties provides effective settlement prevention without adding problematic loads.
Settlement Prevention Benefits:
- Fills voids without adding significant weight to soil systems
- Provides immediate structural support preventing further settlement
- Maintains flexibility to accommodate minor ground movement
- Distributes loads uniformly across treatment areas
- Prevents progressive failure and expanding settlement zones
Installation and Application Advantages
The installation process for polyurethane void filling offers significant advantages over cement grout in terms of equipment requirements, access needs, and operational disruption.
Injection Process Comparison
Polyurethane injection requires minimal access and creates less disruption than cement grouting operations.
Process Differences:
- Hole size: Polyurethane uses dime-sized holes, cement requires larger access points
- Equipment footprint: Polyurethane uses compact equipment, cement needs heavy machinery
- Material handling: Polyurethane is pre-mixed and ready to use, cement requires on-site mixing
- Quality control: Polyurethane expansion is self-evident, cement placement verification difficult
Access Requirements and Site Constraints
Limited access situations often favor polyurethane applications due to reduced equipment and space requirements.
Access Advantages:
- Smaller injection equipment fits in confined spaces
- Minimal surface disruption preserves landscaping and paving
- Reduced excavation needs lower environmental impact
- Faster mobilization and demobilization saves time and cost
- Work possible in occupied buildings with minimal disruption
Traffic and Operational Impact
Infrastructure projects require consideration of traffic control and operational continuity during void filling operations.
| Impact Factor | Polyurethane | Cement Grout | Project Benefit |
| Lane Closure Time | Hours | Days to weeks | Reduced traffic impact |
| Access Restrictions | Minimal | Extensive | Lower control costs |
| Service Interruption | Brief | Extended | Better operational continuity |
| Safety Zone Requirements | Small | Large | Reduced project footprint |
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
While polyurethane material costs may be higher per unit volume, the total project cost often favors polyurethane due to reduced labor, equipment, and indirect expenses.
Direct Cost Comparison
Understanding both material and installation costs provides accurate project cost comparisons between polyurethane and cement grouting approaches.
Cost Factors:
- Material cost per cubic foot: Polyurethane higher, cement lower
- Installation labor: Polyurethane much faster, cement slower and more complex
- Equipment costs: Polyurethane minimal, cement substantial
- Traffic control: Polyurethane brief, cement extended and expensive
- Total project cost: Polyurethane often lower despite higher material cost
Long-Term Value Analysis
Lifecycle cost analysis often shows polyurethane providing superior value through reduced maintenance requirements and extended service life.
Long-Term Benefits:
- Fewer repair cycles due to superior durability
- Reduced maintenance access and traffic control costs
- Better performance under dynamic loading conditions
- Lower risk of progressive failure requiring major repairs
- Extended service life reducing replacement frequency
Professional pressure grouting contractors can provide detailed cost analysis comparing polyurethane and cement approaches for specific project requirements and conditions.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Modern construction increasingly considers environmental impact and sustainability factors in material selection decisions.
Carbon Footprint and Environmental Impact
Polyurethane void filling typically has lower environmental impact than cement grouting due to reduced material transportation and installation equipment requirements.
Environmental Advantages:
- Lower embodied carbon content per unit of structural performance
- Reduced transportation requirements for materials and equipment
- Minimal excavation and site disturbance
- Potential for sustainability credits in green building projects
- Longer service life reducing replacement frequency
Waste Generation and Site Impact
Construction projects increasingly focus on minimizing waste generation and site impact during installation.
Waste Reduction Benefits:
- Precise material placement reduces waste generation
- Minimal excavated material requiring disposal
- Reduced packaging waste from concentrated materials
- Lower fuel consumption from shorter project duration
- Preservation of existing site features and landscaping
Application-Specific Performance
Different void filling applications may favor polyurethane or cement based on specific performance requirements and site constraints.
Slab Stabilization and Lifting
Slab lifting and stabilization applications particularly benefit from polyurethane's lightweight and expansion characteristics.
Slab Application Benefits:
- Precise lifting control through expansion characteristics
- Minimal added load preventing further settlement
- Immediate structural support allowing quick service restoration
- Superior performance in wet conditions common under slabs
- Long-term stability without cracking or deterioration
Underground Utility Protection
Void filling around underground utilities requires materials that provide protection without adding excessive loads or causing access problems.
Utility Protection Advantages:
- Lightweight fill prevents damage to existing utilities
- Chemical compatibility with utility materials and coatings
- Water resistance prevents erosion and washout around utilities
- Flexible properties accommodate thermal expansion and ground movement
- Easy access for future utility maintenance or replacement
Infrastructure Foundation Support
Critical infrastructure foundations require void filling materials that provide reliable long-term support without creating additional problems.
Foundation Support Benefits:
- Immediate load transfer and structural support
- Prevention of progressive settlement and failure
- Compatibility with existing foundation materials
- Long-term durability under dynamic loading
- Minimal maintenance requirements for critical applications
Professional Selection and Application
Achieving optimal results with polyurethane void filling requires professional expertise in material selection, application procedures, and quality control verification.
Material Selection and Formulation
Different polyurethane formulations offer varying characteristics that must match specific application requirements and environmental conditions.
Selection Factors:
- Expansion ratio and final density requirements
- Cure time and working time needs
- Environmental conditions and temperature range
- Chemical compatibility with existing materials
- Load-bearing and structural requirements
Quality Control and Performance Verification
Professional installation includes comprehensive quality control measures that verify void filling effectiveness and predict long-term performance.
Quality Assurance Methods:
- Pre-injection void assessment and mapping
- Real-time monitoring during injection and expansion
- Post-injection testing and performance verification
- Long-term monitoring and evaluation programs
- Warranty coverage for installation effectiveness
Conclusion
Polyurethane beats cement grout for void filling through superior expansion characteristics, dramatically lighter weight, faster cure times, and better water resistance properties. These advantages translate into more effective void filling, reduced project costs, and better long-term performance for most applications.
The combination of rapid installation, minimal disruption, and excellent long-term durability makes polyurethane the preferred choice for critical infrastructure void filling projects. Professional material selection and application ensure optimal results for specific site conditions and performance requirements.
Superior Grouting provides expert polyurethane void filling services utilizing advanced materials and application techniques for optimal project outcomes. For professional evaluation of your void filling needs and material recommendations, contact our experienced team.