Why Cellular Grout Is Ideal for Abandoned Pipe and Tunnel Backfill
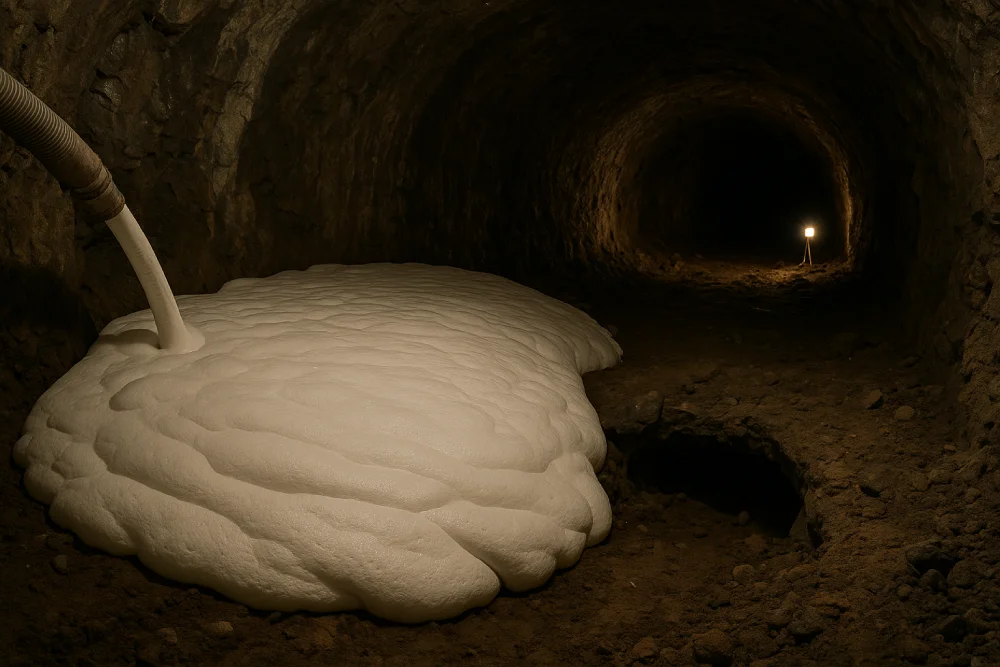

Cellular grout is ideal for abandoned pipe and tunnel backfill because its lightweight flowable consistency fills complex voids completely through remote pumping, prevents subsidence through reduced loads, stops contamination migration, and solidifies rapidly without requiring excavation access or layer-by-layer placement that traditional methods demand.
Aging infrastructure creates a growing challenge as obsolete pipes, conduits, and tunnels reach the end of their service lives. Simply abandoning these underground voids in place creates serious risks including ground subsidence, sinkhole formation, contamination pathway creation, and structural instability threatening overlying buildings, roads, and active utilities.
Traditional abandonment approaches involving excavation and removal prove prohibitively expensive when structures extend deep underground or pass beneath critical infrastructure. Filling with conventional materials like sand or gravel faces severe limitations accessing remote void areas, achieving complete filling, and preventing future settlement from material consolidation.
Cellular grouting provides purpose-built solutions addressing abandoned structure challenges through properties specifically suited to void filling applications. The material's flowability reaches inaccessible areas, its lightweight nature prevents additional loading, and its rapid solidification creates stable masses preventing future ground movement.
Understanding why cellular grout excels for pipe and tunnel abandonment helps agencies and contractors select appropriate methods for the thousands of abandonment projects required as infrastructure systems age and require replacement. Cellular grouting services deliver reliable abandonment solutions protecting public safety while controlling costs.
Key Takeaways
- Flowable consistency allows cellular grout to travel hundreds of feet horizontally through small injection ports, filling entire abandoned pipe and tunnel lengths without requiring excavation access at multiple locations that would disrupt traffic and cost millions in restoration expenses.
- Low density (30-70 pcf) reduces imposed loads by 60-85% compared to traditional fill materials, preventing additional stress on weak soils that could trigger subsidence or damage adjacent structures, utilities, and foundations in urban environments where abandoned infrastructure typically exists.
- Complete void filling eliminates pathways for groundwater flow and contaminant migration that abandoned pipes and tunnels would otherwise provide, protecting water supplies and preventing environmental contamination that creates cleanup liabilities exceeding $500,000-5,000,000 for typical abandoned utility projects.
- Rapid setting within 2-24 hours creates stable masses that prevent future ground movement from void collapse or material consolidation, eliminating the ongoing sinkhole risks that threaten public safety and create emergency repair costs averaging $50,000-200,000 per incident.
- Remote pumping through small access points eliminates extensive excavation required for conventional backfill placement, reducing project costs by 40-70% through avoided excavation, shoring, traffic control, and street restoration that would otherwise dominate project budgets.
- Buoyancy force reduction from lightweight cellular grout prevents flotation of carrier pipes in high-water conditions, a critical concern for water and sewer systems where pipe stability affects adjacent active utilities and prevents cascading failures in interconnected infrastructure networks.
The Challenge of Abandoned Underground Infrastructure
Recognizing the specific problems abandoned pipes and tunnels create establishes context for why cellular grout provides superior solutions.
Extent of Aging Infrastructure
Infrastructure systems built 50-100 years ago are reaching the end of their design lives simultaneously, creating massive abandonment needs. Major cities contain hundreds of miles of obsolete pipes, utility tunnels, and abandoned transit systems requiring proper decommissioning.
The scope challenges project planning and budgets:
- Scale of inventory: Large metropolitan areas may have 200-500 miles of pipes and tunnels requiring abandonment
- Access difficulties: Structures pass beneath buildings, active roadways, and operating utilities complicating access
- Budget constraints: Proper abandonment competes with new construction for limited infrastructure funding
- Regulatory requirements: Environmental regulations mandate proper closure preventing contamination pathways
- Public safety concerns: Void collapse creates sinkholes endangering lives and disrupting services
These factors create pressure for abandonment methods that work reliably while controlling costs and minimizing disruptions.
Risks of Improper Abandonment
Simply leaving abandoned structures in place without proper filling creates predictable and expensive consequences.
Subsidence and Sinkhole Formation:
Empty pipes and tunnels represent voids in soil that eventually collapse as surrounding material erodes into the space or structural deterioration allows roof collapse. Surface subsidence and sinkholes appear suddenly, often without warning:
- Pavement collapse swallowing vehicles and endangering drivers
- Building foundation undermining causing structural damage
- Utility line breaks from differential settlement
- Casualties from sudden ground collapse in pedestrian areas
Emergency repairs for sinkhole-related damage typically cost $50,000-200,000 per incident excluding liability claims. Major sinkholes in urban areas can reach $1-5 million in total costs including emergency response, repairs, and business disruption.
Contamination Migration Pathways:
Abandoned pipes create preferential flow paths for groundwater and contaminants. Pollutants from surface spills, leaking underground storage tanks, or historical industrial sites migrate rapidly through pipe networks contaminating much larger areas than would occur through soil alone:
- Drinking water supply contamination requiring extensive remediation
- Vapor intrusion into buildings from volatile contaminants
- Accelerated plume migration increasing cleanup scope and costs
- Regulatory violations and enforcement actions
Environmental cleanup triggered by contamination migration through abandoned structures routinely costs $500,000-5,000,000 and can reach tens of millions for large plumes affecting multiple properties.
Adjacent Structure Instability:
Loss of ground support from abandoned structure voids causes settlement and instability of nearby active utilities, building foundations, and transportation infrastructure. This cascading failure phenomenon creates problems far beyond the immediate abandoned structure location.
Regulatory and Liability Drivers
Regulations increasingly mandate proper abandonment rather than allowing structures to remain empty in place. State and local codes specify filling requirements, acceptable materials, and verification procedures ensuring abandoned infrastructure does not create future problems.
Liability concerns amplify these regulatory requirements. Property owners and infrastructure agencies face legal responsibility for damages caused by improperly abandoned structures. Insurance coverage may exclude claims related to known abandoned infrastructure not properly addressed, creating direct financial exposure.
These regulatory and liability considerations drive adoption of proven abandonment methods like cellular grouting that reliably prevent future problems rather than cheaper approaches carrying higher long-term risks.
Why Cellular Grout Properties Match Abandonment Needs
The unique characteristics of cellular grout directly address the specific challenges abandoned pipe and tunnel filling presents.
Unmatched Flowability for Remote Access
The most critical requirement for abandoned structure filling is reaching all void areas from limited access points. Excavating access at frequent intervals defeats the purpose of in-place abandonment and creates costs approaching complete removal and replacement.
Cellular grout's consistency resembles thick pancake batter or milkshake, flowing easily through pipes and tunnels for distances of 500-2,000 feet from single injection points. This flowability results from:
- Low viscosity: Minimal resistance to flow compared to concrete or conventional grout
- Air bubble suspension: Cellular structure maintains fluidity during pumping
- Controlled setting time: Formulations remain flowable 2-6 hours allowing extended pumping operations
- Minimal friction loss: Smooth flow characteristics prevent excessive pressure buildup
This remote filling capability means:
- Single injection point can fill 1,000+ feet of pipe length
- Minimal excavation limited to injection access locations
- Reduced traffic and utility disruptions
- Lower restoration costs from fewer excavation sites
- Faster project completion through continuous filling operations
Comparison with Traditional Methods:
The table below illustrates flowability advantages for a typical 36-inch diameter abandoned sewer line, 2,000 feet long:
| Fill Method | Maximum Flow Distance | Required Access Points | Excavation Quantity | Project Duration |
| Cellular Grout | 1,000-2,000 feet | 1-2 locations | 100-200 cubic yards | 2-3 days |
| Sand Slurry | 200-400 feet | 5-10 locations | 500-1,000 cubic yards | 1-2 weeks |
| Flowable Fill (CLSM) | 400-800 feet | 3-5 locations | 300-500 cubic yards | 3-7 days |
| Granular Fill | 0 feet (no flow) | Continuous access | Full excavation required | 4-8 weeks |
The cellular grout advantage becomes overwhelming when considering total project costs including excavation, shoring, traffic control, and restoration that dominate conventional method expenses.
Lightweight Properties Preventing Additional Loading
Abandoned pipes and tunnels often exist in weak soils or areas where additional loading would trigger settlement or bearing failure. The structures themselves may have provided some ground support that their removal eliminates, creating stability concerns.
Cellular grout's low density (30-70 pounds per cubic foot) imposes minimal additional load on surrounding ground:
- 60-85% lighter than traditional fill: Dramatically reduced stress on weak soils
- Minimal settlement risk: Lightweight fill prevents consolidation of underlying compressible soils
- Reduced lateral pressures: Less horizontal stress on adjacent structures and utilities
- Buoyancy benefits: Near-neutral density in saturated conditions prevents flotation forces
Load Comparison Example:
A 48-inch diameter tunnel, 10 feet deep, filled for 1,000 feet length:
- Cellular grout (50 pcf): 164 tons total weight, 820 psf on tunnel invert
- Sand fill (100 pcf): 327 tons total weight, 1,640 psf on tunnel invert
- Concrete (150 pcf): 491 tons total weight, 2,460 psf on tunnel invert
The cellular grout places one-third the load of sand and one-sixth the load of concrete, often making the difference between acceptable performance and ground failure in weak soil conditions.
Rapid Solidification Creating Stable Masses
Abandoned structure filling must create stable masses that will not consolidate, settle, or migrate over time. Material that remains fluid or consolidates significantly defeats the purpose of void filling by creating new voids as the fill material settles.
Cellular grout sets and gains strength rapidly through controlled chemical reactions:
- Initial set: 30 minutes to 4 hours depending on formulation
- Working strength: 24-72 hours for light loading
- Design strength: 7-28 days for full capacity
- Long-term stability: Minimal consolidation or volume change over decades
This rapid strength development enables:
- Quick return to service of overlying pavements and structures
- Immediate ground stabilization preventing progressive collapse
- Early verification that void filling succeeded before project completion
- Minimal construction disruption windows for public facilities
Setting Time Control:
Cellular grout formulations can be adjusted for project-specific requirements:
- Fast-setting (30 minutes-2 hours): Emergency repairs, small volumes, rapid traffic restoration
- Standard-setting (2-6 hours): Most abandonment projects balancing pumping time and strength gain
- Slow-setting (6-24 hours): Very long pipe runs requiring extended pumping operations
This control allows optimization for each project's unique access, volume, and schedule requirements.
Application Methods for Pipe and Tunnel Abandonment
Proper execution of cellular grout abandonment requires systematic approaches tailored to specific structure types and conditions.
Abandoned Pipe Filling Procedures
Pipe abandonment using cellular grout follows established procedures ensuring complete filling and proper documentation.
Pre-Filling Preparation:
Before grouting begins, pipes require assessment and preparation:
- Video inspection: Camera surveys identify breaks, offshoot connections, and obstructions
- Flow testing: Water flow tests verify pipe integrity and identify major breaks requiring sealing
- Access point creation: Small excavations expose pipe for injection port installation
- Pipe sealing: Major breaks, service connections, and manholes are plugged preventing grout loss
- Monitoring point establishment: Observation ports verify grout arrival and filling completion
Injection Sequence:
Systematic filling approaches ensure complete void occupation:
- Start at lowest elevation: Grout flows upward filling pipes completely to highest point
- Monitor grout emergence: Observation ports confirm grout arrival at expected times
- Continuous injection: Uninterrupted pumping prevents cold joints or incomplete filling
- Pressure monitoring: Track injection pressures detecting blockages or unexpected flow paths
- Volume verification: Compare injected volume to calculated pipe volume confirming complete filling
Quality Verification:
Documentation proves proper abandonment meeting regulatory requirements:
- Injection records showing volumes, pressures, and durations
- Grout sample testing verifying density and strength
- Video confirmation of grout in pipe (where possible)
- Volume reconciliation comparing injected to theoretical amounts
- Professional certification of proper abandonment procedures
Tunnel and Large Structure Abandonment
Larger structures like utility tunnels, subway sections, or mine workings require modified approaches scaling up pipe abandonment procedures.
Access Point Strategies:
Large volumes benefit from multiple injection points working simultaneously:
- Portal access: Existing entrances provide primary injection locations
- Shaft access: Vertical shafts allow filling from multiple elevations
- Strategic excavations: Limited excavations create intermediate access reducing total pumping distances
- Sequential filling: Progressive filling from lowest to highest areas ensures complete occupation
Volume and Rate Management:
Large structure filling involves substantial material quantities requiring logistics planning:
The table below shows typical parameters for tunnel abandonment projects:
| Tunnel Size | Volume per 1,000 ft | Injection Rate | Fill Duration | Material Cost | Total Project Cost |
| 6 ft diameter | 880 cubic yards | 30-50 cy/hour | 1-2 days | $250,000-350,000 | $400,000-600,000 |
| 10 ft diameter | 2,450 cubic yards | 50-100 cy/hour | 2-4 days | $600,000-1,000,000 | $1,000,000-1,500,000 |
| 15 ft diameter | 5,500 cubic yards | 100-150 cy/hour | 4-7 days | $1,400,000-2,200,000 | $2,000,000-3,000,000 |
These volumes require:
- Multiple concrete pump trucks for continuous supply
- Batch plant coordination ensuring consistent material properties
- Quality control testing throughout multi-day operations
- Traffic and access management for sustained trucking operations
- Contingency planning for equipment failures or weather delays
Structural Considerations:
Large abandoned tunnels may contain internal structures requiring special attention:
- Rails and utilities: Existing equipment and services embedded in cellular grout
- Ventilation systems: Ductwork and mechanical equipment filled along with main tunnel
- Support structures: Steel sets, timber blocking, or concrete lining surrounded by grout
- Compartmentalization: Bulkheads divide tunnels into manageable filling sections
These elements complicate volume calculations and may create flow restrictions requiring additional access points.
Environmental Protection Benefits
Cellular grout abandonment provides specific environmental advantages beyond just filling void spaces.
Groundwater Contamination Prevention
Empty abandoned pipes and tunnels create preferential flow paths allowing rapid contaminant migration through subsurface environments. Cellular grout filling eliminates these pathways protecting groundwater resources.
Mechanism of Protection:
Cellular grout's low permeability (10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁷ cm/sec) prevents significant water flow through filled structures:
- Contaminant plumes encountering filled pipes cannot migrate rapidly through the structure
- Groundwater flow reverts to natural soil pathways with much slower velocities
- Time for natural attenuation increases dramatically slowing contamination spread
- Pumping and treatment systems can contain plumes without fast pathway short-circuits
Regulatory Compliance:
Environmental regulations increasingly require abandoned structures that could facilitate contamination be properly filled. Closure permits for industrial facilities, underground storage tank removals, and brownfield redevelopment projects mandate abandonment methods preventing future migration.
Cellular grout's documented low permeability and permanence satisfy regulatory requirements where less complete methods might not gain approval.
Vapor Intrusion Barrier Creation
Volatile contaminants in soil or groundwater can migrate as vapors through abandoned pipes and tunnels into buildings, creating health risks and requiring expensive mitigation. Proper abandonment with cellular grout blocks these vapor pathways.
Vapor Migration Concerns:
Common volatile contaminants creating vapor intrusion risks include:
- Petroleum hydrocarbons (gasoline, diesel, heating oil)
- Industrial solvents (TCE, PCE, other chlorinated compounds)
- Natural gas from leaking utility lines
- Radon from geological sources
Abandoned pipes connecting contaminated soil to building basements or utility vaults create direct pathways allowing vapors to accumulate to hazardous concentrations.
Cellular Grout Vapor Sealing:
The solidified cellular mass blocks vapor migration through multiple mechanisms:
- Physical barrier preventing gas flow through pipe
- Pore structure limiting diffusion of volatile compounds
- Long diffusion path reducing migration rates to negligible levels
- Permanent solution requiring no maintenance or monitoring
This vapor sealing function provides long-term protection without requiring active systems or ongoing costs associated with alternatives like vapor barriers or ventilation systems.
Contaminated Structure Stabilization
Abandoned pipes and tunnels may contain residual contamination from previous use requiring containment during abandonment. Cellular grout encapsulates contaminants preventing mobilization and exposure.
Encapsulation Mechanism:
Contaminants physically trapped within cellular grout matrix cannot migrate:
- Solid cellular structure immobilizes particulate contamination
- Low permeability prevents leaching by groundwater flow
- Chemical stability resists degradation that would release contaminants
- Alkaline pH can chemically stabilize certain contaminant types
This encapsulation approach often proves more economical than complete contamination removal prior to abandonment, particularly for large structures with extensive contamination.
Cost-Effectiveness and Economic Benefits
Cellular grout abandonment typically costs less than alternatives when considering total project expenses and avoided future liabilities.
Direct Cost Comparison
Initial material costs appear higher for cellular grout versus conventional alternatives, but total installed costs tell a different story.
The table below compares complete project costs for abandoning a 36-inch diameter sewer line, 1,000 feet long, 12 feet deep:
| Cost Component | Cellular Grout | Flowable Fill (CLSM) | Sand Slurry | Complete Removal |
| Material | $60,000 | $30,000 | $25,000 | $0 (disposal cost) |
| Excavation | $15,000 (2 sites) | $45,000 (5 sites) | $75,000 (10 sites) | $120,000 (full length) |
| Shoring | $8,000 | $25,000 | $40,000 | $60,000 |
| Traffic Control | $10,000 (1 week) | $25,000 (2 weeks) | $40,000 (3 weeks) | $80,000 (6 weeks) |
| Pumping/Placement | $12,000 | $15,000 | $20,000 | N/A |
| Removal & Disposal | $0 | $0 | $0 | $95,000 |
| Restoration | $20,000 | $60,000 | $100,000 | $150,000 |
| Total Project Cost | $125,000 | $200,000 | $300,000 | $505,000 |
Cellular grout's ability to minimize excavation, shoring, traffic control, and restoration costs makes it economically superior despite premium material pricing.
Avoided Future Costs
Proper initial abandonment prevents expensive future problems that improper or incomplete methods create.
Sinkhole Prevention Value:
Sinkholes from improperly abandoned structures cost $50,000-200,000 for typical repairs including:
- Emergency response and safety measures
- Excavation and void filling
- Utility repairs from breaks caused by collapse
- Pavement and surface restoration
- Traffic control and detour costs during repairs
The probability of sinkhole occurrence over 20-30 years without proper abandonment ranges from 30-70% depending on soil conditions and structure depth. Expected future cost from this risk alone justifies proper initial abandonment with cellular grout.
Environmental Liability Avoidance:
Contamination migration through improperly abandoned structures creates cleanup costs exceeding initial proper abandonment costs by factors of 10-100 times:
- Site investigation: $50,000-200,000
- Remedial design: $100,000-500,000
- Cleanup implementation: $500,000-5,000,000+
- Long-term monitoring: $25,000-100,000 annually
- Legal and regulatory costs: $100,000-1,000,000
Proper cellular grout abandonment preventing this migration provides environmental insurance worth millions in avoided future expenses.
Adjacent Structure Protection:
Settlement from improperly abandoned structures damages nearby active utilities, building foundations, and pavements creating repair costs of:
- Utility line repairs: $5,000-50,000 per break
- Building foundation repairs: $50,000-500,000 per structure
- Pavement rehabilitation: $100-300 per square yard
- Legal claims from affected property owners: Highly variable
The cumulative avoided costs from these damage mechanisms often exceed cellular grout abandonment costs within 5-10 years of project completion.
Schedule Value and Disruption Minimization
Faster project completion reduces time-dependent costs and community disruption creating substantial value beyond direct cost savings.
Time-Dependent Cost Impacts:
Projects requiring extended construction periods accumulate costs through:
- Daily traffic control: $1,000-5,000 per day
- Business access disruption: $500-10,000 per day lost revenue
- Additional inspection and management: $1,000-3,000 per day
- Extended equipment rental: $500-2,000 per day
Cellular grout completing in 2-3 days versus conventional methods requiring 2-6 weeks saves $50,000-300,000 in these time-dependent costs alone.
Community Impact Reduction:
Minimizing construction duration reduces less quantifiable but very real community impacts:
- Reduced traffic congestion and commute delays
- Less noise and dust affecting nearby residents
- Faster return to normal business operations
- Lower political pressure from frustrated stakeholders
These quality-of-life improvements during construction justify cellular grout selection even when direct cost differences appear marginal.
Safety Advantages in Abandonment Operations
Cellular grout application methods provide inherent safety benefits compared to conventional abandonment approaches requiring confined space entry and extensive excavation.
Confined Space Entry Elimination
Traditional abandonment methods often require workers entering pipes and tunnels to prepare structures, install plugs, or verify filling. These confined space entries create significant safety hazards including:
- Atmospheric hazards: Oxygen deficiency, toxic gases, explosive atmospheres
- Physical hazards: Collapse risks, drowning, temperature extremes
- Access challenges: Difficult rescue if emergencies occur
- Regulatory burdens: Extensive permitting, monitoring, and safety equipment requirements
Cellular grout's remote pumping capability eliminates most confined space entries. All injection, monitoring, and verification occurs from surface locations through access ports. This elimination of confined space work provides:
- Removal of most serious safety risks to workers
- Reduced insurance costs from lower risk exposure
- Simplified permitting and regulatory compliance
- Faster operations without confined space safety procedures
- Improved worker acceptance and reduced project liability
Excavation and Shoring Risk Reduction
Extensive excavation required for conventional abandonment methods creates trenching and shoring hazards. Cave-ins represent one of the most deadly construction hazards, causing approximately 40 deaths annually in the United States.
Cellular grout's minimal excavation requirements reduce trenching hazards dramatically:
- Fewer excavations: 1-3 access points versus 5-20 for conventional methods
- Smaller excavations: Limited size for injection equipment access only
- Shallower excavations: Often need only reach pipe crown rather than full depth
- Shorter duration: Excavations open hours to days rather than weeks
This excavation reduction translates directly to reduced worker risk exposure and improved project safety records.
Material Handling Safety
Conventional abandonment materials create handling hazards cellular grout avoids:
Traditional Material Challenges:
- Heavy manual lifting of sand bags or material buckets
- Dust exposure from granular materials
- Repetitive motion injuries from shoveling and spreading
- Equipment hazards from loaders and conveyors
Cellular Grout Advantages:
- Fully mechanized pumping eliminates manual material handling
- Enclosed system prevents dust and exposure
- Minimal physical labor reducing injury risks
- Automated operations removing workers from hazard zones
The safety improvements contribute to lower workers' compensation insurance costs and improved project safety statistics benefiting contractor reputation and future bidding competitiveness.
Future Developments and Emerging Technologies
Cellular grouting technology for abandonment applications continues evolving, expanding capabilities and improving performance.
Smart Monitoring Systems
Emerging sensor technologies enable real-time monitoring of abandonment filling operations:
Flow Visualization:
- Pressure sensors throughout pipe networks verify grout arrival at expected times
- Temperature monitoring detects grout presence through heat of hydration
- Acoustic sensors identify grout flow advancement and potential blockages
- Real-time data displays show filling progress on digital maps
These monitoring systems provide confidence that complete filling occurred without requiring expensive post-filling verification excavations.
Advanced Material Formulations
Research into improved cellular grout properties addresses specific abandonment challenges:
Extended Pumping Time Formulations:
- Setting time control allowing 12-24 hour working periods
- Enables filling extremely long pipe networks from single access points
- Temperature-stable performance in varying conditions
- Predictable strength development after extended pumping operations
Ultra-Lightweight Densities:
- Formulations achieving 20-30 pounds per cubic foot
- Extreme load reduction for most weight-sensitive applications
- Near-neutral buoyancy in saturated conditions
- Specialized applications in high water table areas
Enhanced Permeability Resistance:
- Material modifications reducing permeability to 10⁻⁸ cm/sec or lower
- Superior containment for contaminated structure abandonment
- Improved vapor barrier performance
- Longer-term environmental protection assurance
Robotics and Automation
Autonomous systems may eventually enable abandonment operations with minimal human intervention:
Robotic Inspection:
- Small robots navigating pipes conducting pre-grouting surveys
- Real-time video and sensor data collection
- Automated obstruction identification and documentation
- Plug installation in branches and offshoot connections
Automated Injection Systems:
- Computer-controlled pumps adjusting flow rates based on feedback
- Automatic density monitoring and correction
- Self-documenting operations creating permanent quality records
- Remote operation from above-ground control stations
These technologies will further improve safety by removing workers from hazardous abandoned structure environments while enhancing quality control and documentation.
Conclusion
Cellular grout provides ideal properties for abandoned pipe and tunnel backfill through its unique combination of flowability, lightweight characteristics, rapid setting, and environmental protection. The material reaches remote void areas from limited access points, imposes minimal additional loading on weak soils, solidifies quickly creating stable masses, and prevents contamination migration through completed fills.
These properties translate to practical benefits including lower total project costs despite premium material pricing, dramatically reduced construction timelines, improved safety through eliminated confined space entry and reduced excavation, and prevented future liabilities from subsidence and environmental contamination.
As infrastructure systems age and require decommissioning, proper abandonment methods become increasingly critical for public safety and environmental protection. For projects requiring abandoned structure filling, contact Superior Grouting to discuss how cellular grouting delivers reliable, cost-effective solutions meeting regulatory requirements while protecting communities from future abandonment-related hazards.